If you have bleeding gums, you might have the early stages of gum disease: Gingivitis vs Periodontitis. What’s the Difference?
If you have started noticing sensitivity or bleeding in your gums, you’ve come to the right place. Many people have questions about their hypersensitive and bleeding gums. They want to know the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis and how it may be affecting their oral health.
From causes to treatments – we’ve got answers. Consider this blog your golden guide to pain-free, healthy gums.
Common Doesn’t Mean It’s Good
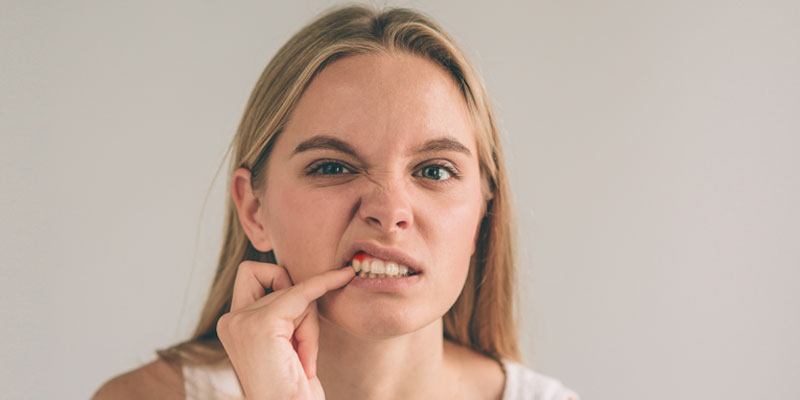
Many people think that it’s normal for their gums to bleed after brushing their teeth. After all, bristles are stiff and pointed enough to scrape sensitive gum tissue, right? Not exactly.
While it can be common to see blood after brushing or flossing, it should not be an everyday occurrence. Recurring bleeding after brushing could be an indicator of chronic gum disease.
But before you sound the alarm, read over the facts, signs, and causes of gum disease below. Learn the difference between gingivitis and periodontitis.
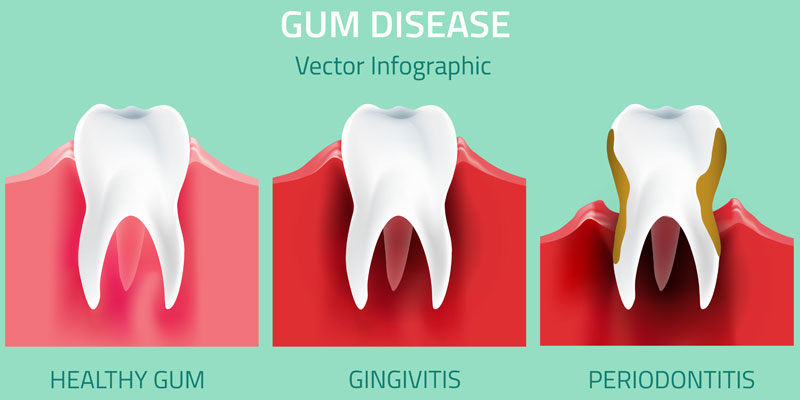
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is a common gum disease affecting adults of all ages. It happens when plaque builds up on our teeth, causing harmful bacteria to collect along gums.
Gingivitis affects your gingiva, the part of your gum around the base of your teeth. It often causes irritation, redness, and swelling.
Signs of Gingivitis
- Gum irritation
- Redness and swelling around your gums
- Gums that often bleed when brushing or flossing
- Tender gums when brushing
- Bad breath
Causes of Gingivitis
Plaque is a bacteria-rich, sticky substance that affects oral tissue at the gum line. It is the main cause of gingivitis.
If plaque is not removed daily, it turns into a harder substance called tartar. Tartar is a combination of plaque, oral bacteria, and saliva minerals.
Tartar develops into a yellowish coating on teeth, and it will end up seeking refuge in your gums.
Risk factors for gingivitis include:
- Neglecting oral health
- Smoking
- Chewing tobacco
- Proneness to dry mouth/lack of saliva
- Nutritional deficiencies/poor eating habits
- Certain medications such as calcium channel blockers or anti-seizure drugs for epilepsy
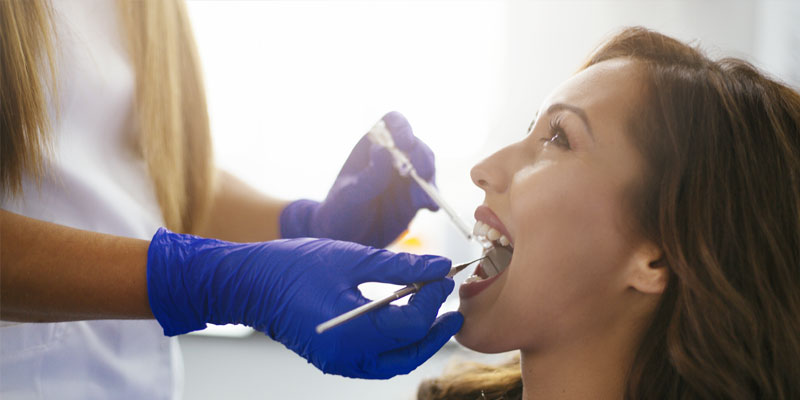
Treatment for Gingivitis
A highly trained professional will perform a scaling and root planing procedure to remove the plaque, tartar, and bacteria growing under the gum line.
Regular dental cleanings will minimize plaque and tartar buildup along with a daily regimen of brushing and flossing.
Prevention of Gingivitis
Practice the following three easy tips to prevent bleeding gums and gingivitis:
Good Oral Hygiene
The number one cause of gum disease is poor oral hygiene. It seems many people forget how important it is to build on good habits.
Proper oral care includes flossing and brushing twice a day. Floss first, then spend at least two minutes brushing your teeth.
To go above and beyond, brush after each meal or snack. This will remove any food particles or bacteria that linger.
If you often forget to keep up with good oral health habits, create reminders on your phone.
Another way to create a reminder is by leaving your toothbrush in a place you can see it. Put your toothbrush, toothpaste, mouthwash, and floss together all in one convenient spot.

Good Health Practices
Many people do not realize how important diet is for our oral health. Certain foods help to reduce bacteria in our mouths and break down tartar.
Learn more about the top foods to eat for your oral health. Knowing which foods are good and bad will help you make better decisions about your diet.
Regular Dental Visits
It’s important to see your dentist twice a year to maintain good oral health. Schedule regular cleanings and checkups every six months.
Talk to your dentist about your best course of treatment. If you have risk factors, you may need to visit more often.
For patients with phobias or anxiety, find a dentist that caters to these issues. At Hamburg Dental Care, we offer a Wand numbing system that makes visits pain and anxiety-free.
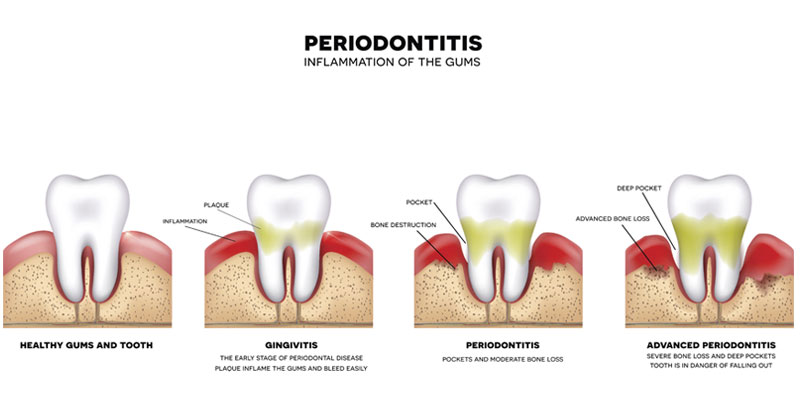
Periodontitis
Periodontal disease is what happens when gingivitis worsens or goes untreated. It is a more serious form of gingivitis where gum tissue and bone separate from teeth.
This separation creates gaps between gums and teeth allowing more bacteria to collect. The collection of bacteria then infects teeth and gums causing irreversible damage.
Periodontal disease is typically seen in adults and it can be very serious if left untreated.
Studies show that bacteria from plaque can enter our bloodstream. Once bacteria enter, it circulates throughout the entire body, causing severe inflammation.
Causes of Periodontitis
The main cause of periodontal disease is bacteria. Harmful bacteria in the mouth infects tissue surrounding our teeth. It then causes the gum around the tooth to become inflamed and painful.
Once bacteria turn to plaque and then to tartar, it makes teeth harder to clean. Then, only a dental professional can clean along your gumlines to remove the bacteria.
Signs of Periodontitis Include:
- Swollen, bright red gums that bleed even when you don’t brush
- Pockets of pus-forming under the gum line
- Receding gums leading to tooth sensitivity
- Halitosis (bad breath)
- Tooth decay/cavities
- Loose teeth
- Pain when chewing on food
Risk Factors for Periodontal Disease:
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Poor oral hygiene
- Stress
- Heredity
- Crooked teeth
- Underlying immune system diseases
- Fillings that have become defective
- Taking medications that cause dry mouth
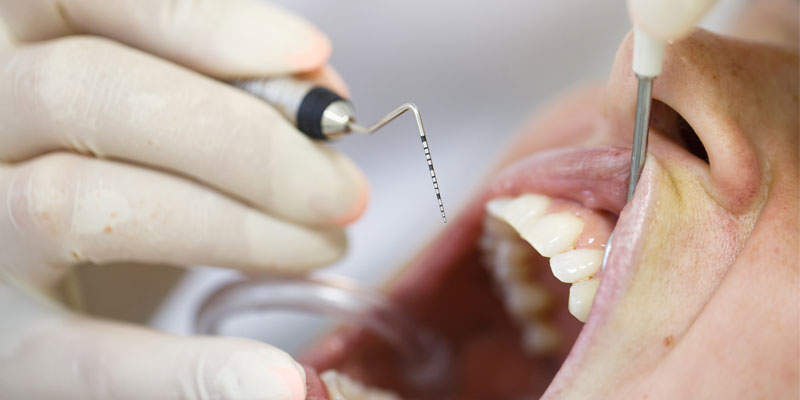
Treatments for Periodontitis
Periodontal Cleaning
During a periodontal cleaning, your dentist will remove plaque and tartar deposits. The goal is to achieve clean teeth both above and below the gumline.
Scaling and Root Planing
Deep cleaning, scaling, and root planning are all used in periodontal cleaning. They get rid of bacteria and allow the gums to close around teeth and heal.
Scaling is the actual removal of plaque and tartar above and below the gumline.
Root planning is the process of eliminating porous spots on teeth where bacteria tend to accumulate.
After a periodontal cleaning, your gums will remain sensitive for a few days. You may find hot or cold foods difficult to eat. This is completely normal.
Antibiotics
In advanced conditions, patients may need to take antibiotics to eliminate the infection. This may add to the length of your recovery time. Once antibiotics begin to take effect, your dentist can begin cleaning treatments.
Implants or Gum Surgery
In the worst conditions, gum disease can cause teeth to loosen or fall out.
Your dentist may recommend a root canal to save teeth with deep cavities. But severely decayed teeth are often extracted and replaced with implants or bridges.
Learn more about root canals and dental implants by reading our blog – Root Canal VS Dental Implant: Choosing the Best Treatment.
Laser gum surgery is available to improve sagging gumlines in extreme cases.
Schedule a Teeth Cleaning and Examination
Bleeding gums may seem like a normal thing. But it could be the indicator of many serious health issues. People often take for granted how easily we can prevent gum disease. It all starts with good oral habits and finding a dentist that accommodates your needs.
When looking for an experienced dental care provider, Sussex County residents can always contact Hamburg Dental Care to learn why your gums are bleeding and how we can help.